Ned Herrmann developed a four-quadrant model of cognitive preferences and a questionnaire called the Herrmann Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI). The Herrmann Brain Dominant Instrument is based on the idea that one part of the brain is dominant over the others.
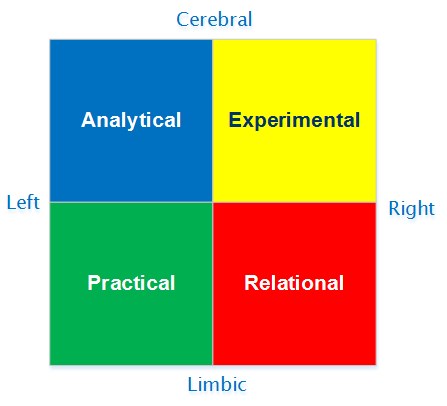
Herrmann created his Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI) based on his Whole Brain Model Theory. He created his model to illustrate that each person’s brain basically has four quadrants when it comes to the process of thinking and learning. The two halves of the brain (right and left) are further divided into a front and back half, making four sections in the brain.
Each of these sections or quadrants are characterized by different learning or thinking styles. Depending on which quadrants you engage, your learning and thinking processes can be significantly different.
Herrmann’s model divides the brain into four different systems with four preferred styles. His model emphasizes the fact that there are really four parts of the brain where dominance’s exist:
A: Left cerebral hemisphere – analytical
B: Left limbic system – sequential
C: Right limbic system – interpersonal
D: Right cerebral hemisphere – imaginative

Brain dominance leads to thinking style preferences, which impact what you pay attention to and how and in what way you learn best.
Each quadrant has preferred learning or thinking activities.
People have varying degrees of dominance in these quadrants. However, individuals are typically more dominant in one of these four areas, which is often manifested by his or her personality type.
However, although a person may be dominant in one area, the research has found that people often use more than one style or quadrant. In fact, most people have primary and secondary preferences for quadrants.
A person may have a primary preference which is an areas of the brain he or she goes too easily and is comfortable with. They also will typically have secondary preferences which are areas of the brain that can be accessed when necessary. There are also preferences which a person may have difficulty accessing or may avoid using.
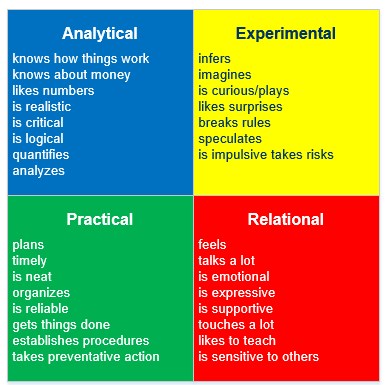
Individuals are dominant in one of these four areas, which is evident by their personality type.
Quadrant A: Theorists (analytical)
Quadrant B: Organizers (sequential)
Quadrant C: Humanitarians (interpersonal)
Quadrant D: Innovators (imaginative)
Theorists – Prefers lecture, facts, and details, critical thinking, textbooks and readings, etc. They are factually-oriented learner, takes a logical, analytical, quantitative approach to learning tasks
Organizers – prefer to learn by outlining, checklists, exercises and problem solving with steps, policies, and procedures. They learn in a sequential and organized way, and when instructional exercises are structured and detailed.
Humanitarians – prefer brainstorming, metaphors, illustrations and pictures, mind mapping and synthesis, and holistic approaches. They are interpersonal, emotional and kinesthetic.
Innovators – Prefer cooperative learning and group discussion, role-playing, and dramatization. They take a holistic approach and are very visual.